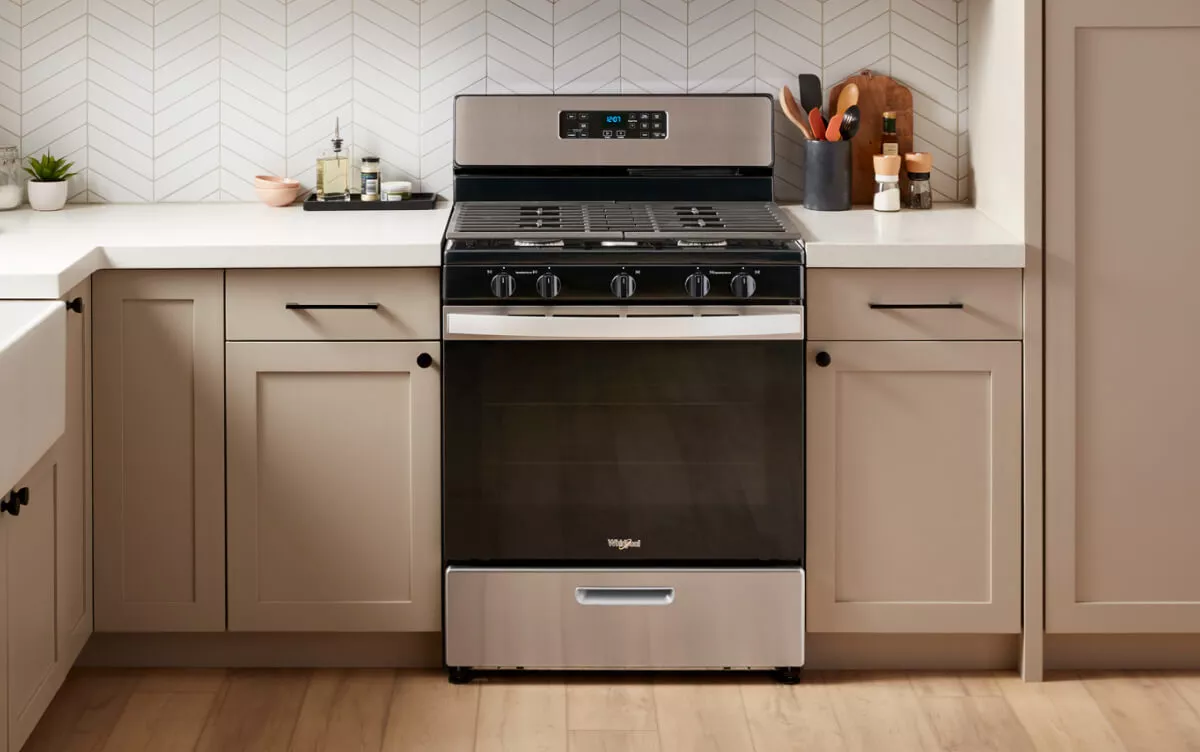
Understanding the different parts of your kitchen stove can help you use it more effectively and efficiently. Whether you’re a seasoned chef or a beginner cook, knowing how your stove works can empower you to create delicious meals with confidence. A kitchen stove is an essential appliance in most homes, serving as the cornerstone of meal preparation. This versatile piece of equipment provides the means to boil, fry, sauté, and simmer a variety of dishes. Its components are designed to work in harmony, ensuring a smooth cooking experience. Understanding the parts and functions of a kitchen stove can aid in its operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Both gas and electric stoves have similar basic parts, including burners or cooktop elements for cooking food, control knobs for regulating temperature, and an oven for baking. However, the details of these components can vary significantly depending on the type of stove. For instance, gas stoves typically feature cast-iron grates over the burners to support cookware, while electric stoves may have a smooth ceramic-glass surface or coiled burners.

Getting to Know Your Kitchen Stove
Regular maintenance of a kitchen stove involves simple yet crucial tasks. Cleaning the oven interior, wiping down the control panel, and checking the integrity of cooktop elements or burners can prolong the appliance’s life and ensure consistent cooking results. Promptly addressing common issues like uneven heating or malfunctioning knobs can prevent larger problems, making familiarity with the stove’s parts invaluable.
The Cooktop
The cooktop is the heart of your stove, where the cooking magic happens. It’s the flat surface on top where you place your pots and pans. There are two main types of cooktops: gas and electric. Gas cooktops use open flames fueled by natural gas or propane, while electric cooktops use heating elements to generate heat. Both types have their own advantages, with gas offering more precise temperature control and electric being easier to clean.
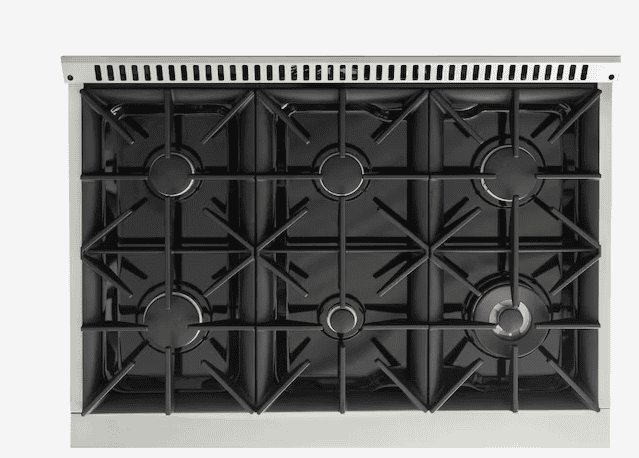
Burners (Gas Cooktops)
Gas cooktops have burners, which are the individual components that produce the flames. They come in different sizes to accommodate various pot and pan sizes. Each burner has a control knob that allows you to adjust the flame intensity, giving you precise control over the heat output.
Heating Elements (Electric Cooktops)
Electric cooktops use heating elements to generate heat. These elements can be coil burners, smoothtop burners, or induction burners. Coil burners are the traditional type, with exposed coils that heat up. Smoothtop burners have a flat, ceramic glass surface that covers the heating elements, making them easier to clean. Induction burners use electromagnetic fields to heat the cookware directly, offering the most efficient and responsive heating.
The Oven
The oven is the enclosed space below the cooktop where you bake, roast, and broil food. It has a heating element, usually located at the bottom, and a thermostat to control the temperature. Most ovens also have a broiler, which is a heating element located at the top of the oven, used for broiling and grilling food.
Oven Racks
Oven racks are the shelves inside the oven where you place your food. They are adjustable to accommodate different dish sizes and cooking needs.
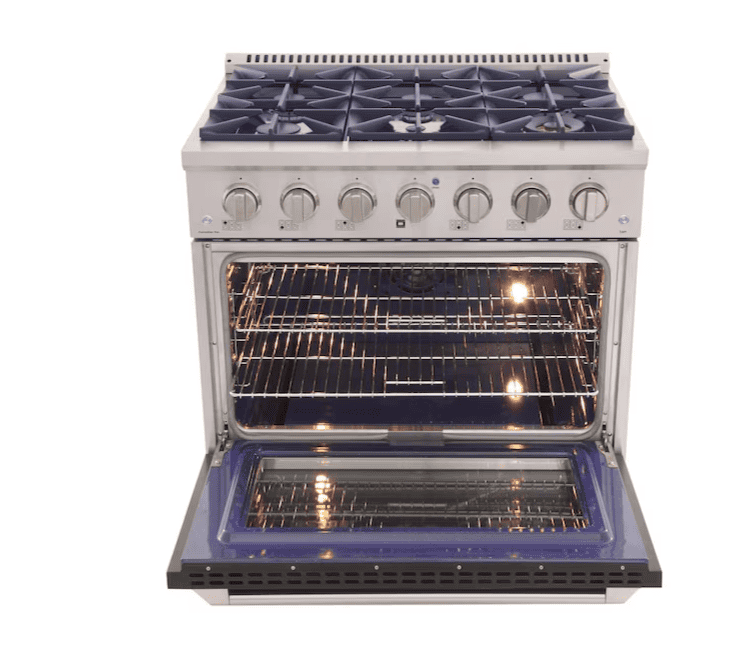

The Control Panel
The control panel is where you operate your stove. It typically includes knobs or buttons for controlling the burners and the oven. Many modern stoves also have digital displays and touch controls for more precise settings and features like timers and preheat alerts.
Other Parts
In addition to these main components, kitchen stoves may also have other features like:
- Drip pans: These are located under the burners on gas cooktops to catch spills and make cleaning easier.
- Grates: These are the metal supports on gas cooktops that hold the cookware above the flames.
- Warming drawer: Some stoves have a warming drawer located below the oven to keep cooked food warm.
- Storage drawer: Some stoves have a storage drawer at the bottom for storing pots and pans.
Table: Common Parts of a Kitchen Stove
| Part | Function | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Cooktop | Surface for cooking with pots and pans | Gas or Electric |
| Burner (Gas) | Produces flames for cooking | Gas |
| Heating Element (Electric) | Generates heat for cooking | Electric |
| Oven | Enclosed space for baking, roasting, and broiling | Gas or Electric |
| Oven Rack | Shelf for holding food inside the oven | Both |
| Control Panel | Interface for operating the stove | Both |
| Drip Pan | Catches spills under the burners | Gas |
| Grate | Supports cookware above the flames | Gas |

Parts of a Kitchen Stove
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Cooktop | The flat surface on top of the stove where the burners or heating elements are located. |
| Burners (Gas Stoves) | The heating elements on a gas stove that use gas flames to cook food. |
| Heating Elements (Electric Stoves) | The electric heating elements on an electric stove that generate heat to cook food. These can be coils, radiant heat elements, or smooth-top surfaces. |
| Grates | The metal bars that sit on top of the cooktop and hold pots and pans in place. |
| Knobs | The knobs that control the gas flow (gas stoves) or power level (electric stoves) of the burners or heating elements. |
| Oven | The enclosed compartment below the cooktop that is used for baking, roasting, and broiling food. |
| Oven Door | The hinged door that provides access to the oven cavity. |
| Oven Racks | The horizontal metal bars inside the oven that hold baking sheets, pans, and other cookware. |
| Drip Pan (optional) | A metal pan located beneath the cooktop that catches spills and drippings from cooking. |
| Broiler (optional) | A heating element located at the top of the oven cavity that is used for broiling food. |
Key Takeaways
- A kitchen stove is fundamental for various cooking methods and requires understanding to operate effectively.
- Stove components differ between gas and electric models but share similar functions in cooking and temperature control.
- Routine maintenance and knowledge of stove parts can lead to efficient use and longevity of the appliance.
Types and Functionality
Kitchen stoves come in various models, each offering different features for cooking. Their designs impact how they heat food and how much control a cook has over the cooking temperature.
Gas Stoves
Gas stoves feature burners that can be either open or sealed. Open burners have a visible flame directly under the cookware, providing immediate heat which is easy to adjust. On the other hand, sealed burners are surrounded by a bowl that catches spills and allows for easier cleaning. These stoves use a grate over the burners to support cookware. Gas stoves are praised for their quick temperature control.
- Temperature Control: Dials or knobs allow for precise adjustments.
- Grates: Typically made from cast iron for even heat distribution.
- Burners: Gas provides heat through direct flame contact.
Electric Stoves
Electric stoves have burners, referred to as heating elements, which convert electrical energy into heat. These are usually coil-shaped or smooth-top radiant burners sitting beneath a ceramic surface. The temperature on an electric stove is managed by controls that regulate the flow of electricity.
- Heating Element: Provides heat when electric current runs through it.
- Controls: Knobs or digital touchpads set the heat level.
- Drip Pan: Catches spills, often found under coil burners.
Induction Stoves
Induction stoves use magnetic fields to directly heat cookware. The surface remains comparatively cool as heat is generated within the pan itself. This reduces cooking time and can improve safety in the kitchen. Induction cooktops also offer precise temperature control.
- Induction Cooktop: Heats cookware through electromagnetic energy.
- Controls: Available as touchpads for setting precise temperatures.
- Efficiency: Cookware heats up quickly and with less energy waste.
Ranges with Ovens
Combining a stove and an oven, ranges offer a full cooking experience in one appliance. The oven compartment typically has a door, thermostat for temperature control, and distinct heating elements for baking and broiling.
- Thermostat: Monitors and adjusts the oven temperature.
- Bake Element: Located at the bottom for consistent baking heat.
- Broiler: Positioned at the top of the oven, provides high heat for broiling.
Components and Maintenance
Proper understanding and care of your kitchen stove’s parts are crucial for safety and efficiency. The sections below will guide you through control settings, cleaning routines, and the functional extras that your stove may have.
Control and Settings
Control Panel and Knobs: Usually found on the front or top of the stove, the control panel includes the knobs or digital touchpad that manage the heat levels of the stove elements and oven. A thermostat inside helps maintain the desired temperature. To keep this area in working order, regularly check that the knobs are firmly attached and that the control panel’s display is functioning correctly. If buttons become unresponsive or knobs are loose, they may need replacing.
Cleaning and Replacements
Cleaning Essentials:
- Grates and Drip Bowls: For gas stoves with cast iron grates, wipe them down after each use. If spills occur, remove grates and soak in soapy water before scrubbing. Drip bowls can catch overflow and need regular cleaning.
- Drip Pan and Oven Racks: Clean these parts with a suitable cleaner and cloth. They are often removable for easier cleaning.
- Door: Keep the glass and seals clean to maintain temperature control.
Replacement Parts:
- Look for signs of wear like cracking on burner covers or a stiff oven door. Replace these parts as needed to ensure proper function and safety.
- Remember to match replacement parts like grates or knobs with those designed for your stove model.
Additional Features
- Warming Drawer: Some stoves have a drawer below the oven to keep food warm. Wipe it out regularly and check for any dysfunctional components.
- Accessories and Cookware: Use accessories made for your stove type. For example, flat cookware is essential for good contact on a smooth ceramic-glass cooktop.
By keeping controls clear, maintaining cleanliness, and checking on the functional parts of your stove, you’ll ensure a safe and enjoyable cooking experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section provides clear answers to common questions about kitchen stove components and their functions.
What are the main components found in a gas stove?
Gas stoves typically have a cooktop with burners covered by removable grates, control knobs to adjust the flame, and an oven with racks. They may also have a broiler drawer beneath the oven.
How do the parts of an electric stove differ from a gas stove?
An electric stove may have coiled burners or a flat ceramic-glass cooktop, as well as control knobs or buttons. Unlike gas stoves, electric stoves use electricity to heat the elements and often include a more consistent oven temperature control.
Can you name the elements located on the top of a stove?
The top of a stove, known as the cooktop, often includes burners or heating elements, grates on gas models, and drip pans or bowls to catch spills.
What are the common parts found in a Whirlpool kitchen stove?
A Whirlpool kitchen stove typically comes with elements like burners or heating elements, control knobs, drip bowls, and oven racks. Specific features may vary based on the model.
What functions do the different parts of a kitchen stove serve?
Different parts of a kitchen stove work together to cook food. Burners provide heat for cooking on the cooktop, the oven bakes or roasts with controlled heat, and knobs allow for temperature adjustment.
How is heat regulated in a kitchen stove?
Heat is regulated in a kitchen stove through control knobs or buttons that adjust the gas flame or electrical current to the burners or heating elements, providing precise cooking temperatures.




