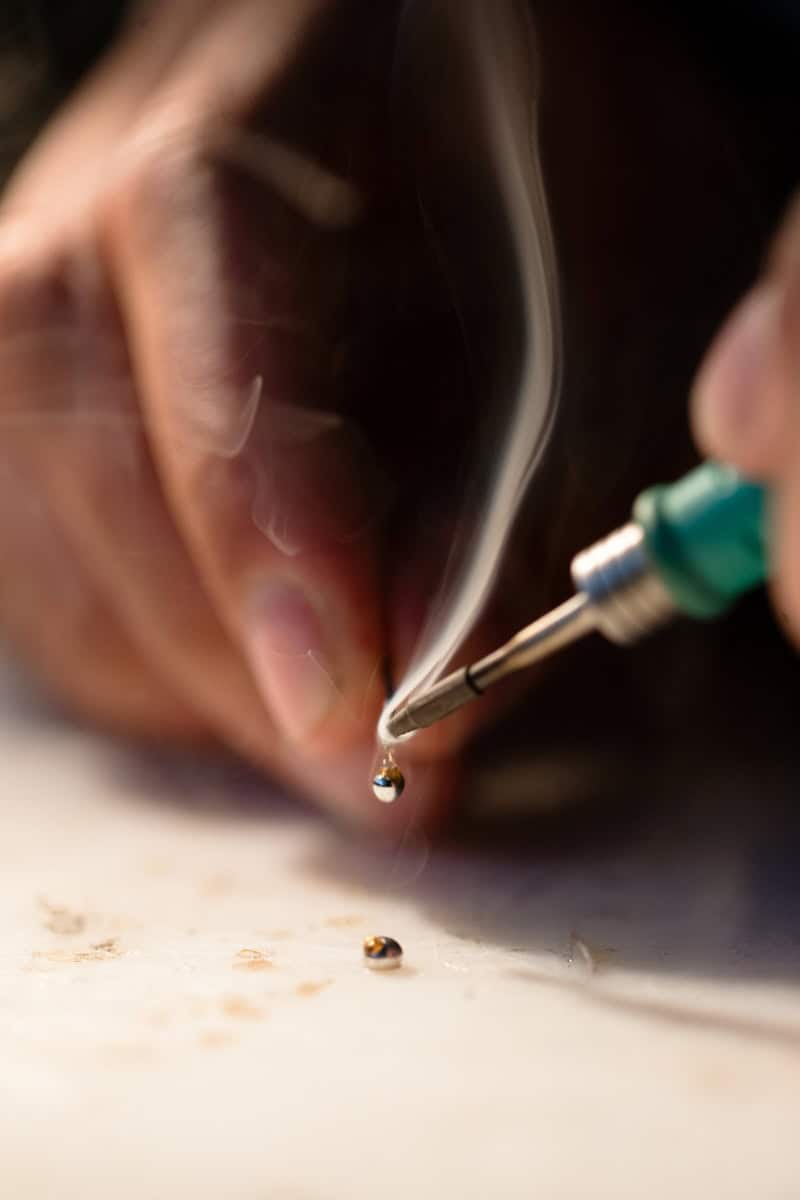
Solder is a versatile material used for many purposes across industries. It is primarily used to join metal parts together, creating strong and reliable connections in various fields. In electronics, solder connects components on circuit boards, ensuring stable electrical pathways.
In plumbing, solder seals metal pipes, preventing leaks and securing plumbing systems. Jewelry makers use solder to piece together delicate items, enabling intricate designs. The aerospace and military sectors also rely on solder for creating durable connections in critical equipment and hardware.
Buildings also benefit from soldered joints in structural applications, enhancing safety and durability. The wide-ranging uses of solder highlight its importance in our daily lives and modern technology.
Composition and Types of Solder
Solder is a metal alloy used to bond metal pieces together. It comes in different materials and types, each designed for specific uses and applications. These types influence its melting point, performance, and safety.
Materials and Alloys
Solder is often made from tin and lead. The most common solder alloy for electronics is 60/40 solder, which is 60% tin and 40% lead. Another popular alloy is 63/37 solder, which has a lower melting point.
There are also lead-free solders made from a mix of metals like tin, copper, silver, and antimony. Lead-free solders have higher melting points and are safer to use.
Different applications need different types of solder. Electronics often use solder wire with additives like flux, while plumbing uses solder with a higher melting point.
| Type of Solder | Melting Point | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| 60/40 (Tin/Lead) | 188°C | Electronics |
| 63/37 (Tin/Lead) | 183°C | Electronics |
| Tin-Copper | 227°C | General Purpose |
| Tin-Silver | 217°C | High Reliability |
Lead-Based and Lead-Free Variants
Lead-based solder is known for its ease of use and reliability. It melts at a low temperature and flows well. However, it is toxic and not safe for plumbing.
Lead-free solder is used more often today because it is safer. It is typically made from elements like tin, copper, and silver. These solders need higher temperatures to melt but are better for the environment and safer for health.
Eutectic solders, like 63/37, melt and solidify at a single temperature. This property makes them perfect for precise electronic work.
Non-eutectic solders have a range of melting points and are often used in other applications.
In summary, choosing between lead-based and lead-free solder depends on the specific needs of the project, including safety and use case. For electronics, rosin core solder is commonly selected for its efficiency and ease.
Applications and Techniques
Soldering is an essential process in both electronics and plumbing. Each field uses specific techniques and materials to create durable bonds.
Soldering in Electronics
Soldering is vital in electronics for connecting components on printed circuit boards (PCBs). A soldering iron is often used to heat the solder, which melts and flows to connect wires and components to the board.
Flux-core solder is popular in electronics because it helps remove oxidation from metal surfaces. This ensures better wetting properties, resulting in stronger bonds. Commonly used solders include tin-lead and lead-free options. Tin-lead solder is flexible and provides excellent conductivity, whereas lead-free solder is safer due to the reduction of lead poisoning risks.
A common issue in electronics is tin whiskers, which are tiny metal fibers that can cause short circuits. Using lead-free solder reduces this risk, complying with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive) standards. For mass production, wave soldering is often employed. This method immerses the PCB in a wave of molten solder to form numerous connections simultaneously.
Plumbing and Pipe Work
In plumbing, soldering is used to join copper pipes and fittings, ensuring a water-tight bond. Plumbers often use a propane torch as a heat source to melt the solder. Plumbing solders typically include lead-free alloys since they must meet safety standards for drinking water.
A critical tool in plumbing is flux, which cleans the pipe surfaces and helps the solder flow more smoothly. Acid core flux is frequently used in plumbing as it effectively removes oxidation from metal surfaces. Illnesses due to lead poisoning can be avoided by using lead-free solder in plumbing applications.
Plumbing work requires very strong joints to handle water pressure. Heating is carefully controlled to avoid damaging the pipes. Proper ventilation and goggles are crucial when soldering in plumbing to ensure safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solder is widely used in electrical applications and has specific materials and properties that make it suitable for the job. Here’s a closer look at these aspects.
Why is solder utilized in electrical applications?
Solder is commonly used in electrical work because it creates a strong bond between metal parts. It also ensures good conductivity which is important for reliable electrical connections. The use of a soldering iron to melt solder helps attach components efficiently.
What materials constitute the composition of solder?
Solder is typically made from a mixture of metals. Traditional solder contains tin and lead. Today, there are also lead-free options available which include metals like tin, silver, and copper. Each type has its own melting point and properties, making them suitable for different applications.
How is soldering different from welding?
Both soldering and welding join metal parts, but they are different processes. Soldering uses a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the metals being joined. Welding, on the other hand, involves melting the base metals themselves. Soldering is ideal for electronics, whereas welding is used for structural applications.
What are the common types of solder used in electronics?
Several types of solder are used in electronics. Leaded solder, typically a tin-lead mix, is popular for its ease of use. Lead-free solder, often made from tin, silver, and copper, is becoming more common due to health and environmental concerns. Rosin-core solder combines solder with flux to help the solder flow more easily around components.
What are the defining properties of solder?
Solder has several important properties. It has a low melting point, allowing it to melt easily with a soldering iron. It also has good electrical conductivity which is critical for electronic circuits. The strength of the bond it creates once cooled is another key property.
What is the composition of lead-free solder?
Lead-free solder is commonly made from a mix of tin, silver, and copper. This combination is often referred to as SAC solder. SAC stands for the chemical symbols of Tin (Sn), Silver (Ag), and Copper (Cu). This composition avoids the use of lead, making it safer for health and the environment.