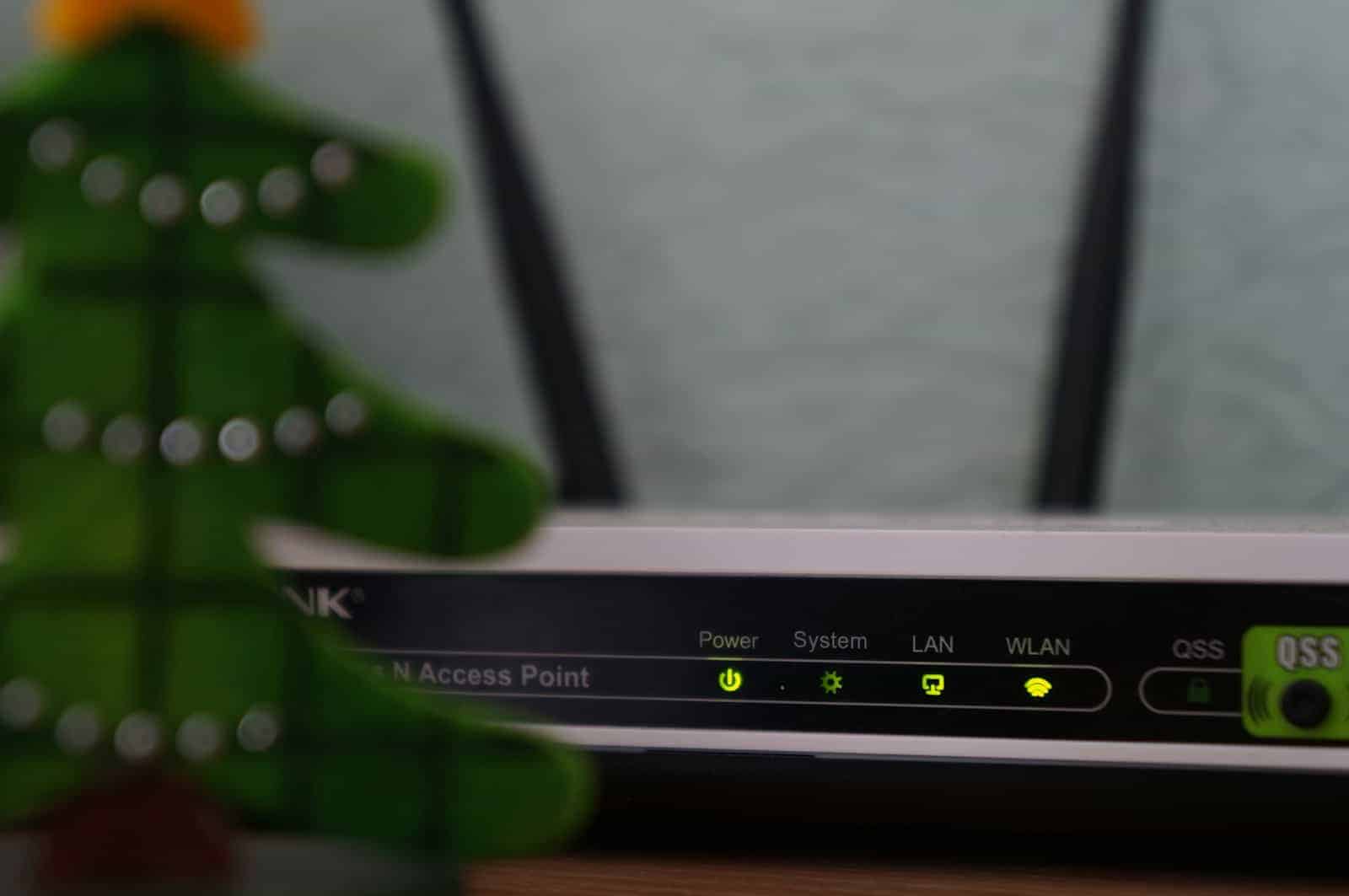
To set up a wireless network using a router and a modem, you need to follow a few steps. This creates a network that allows multiple devices to access the internet without using cables. In this guide, we’ll cover configuring your modem to work in bridge mode if needed and setting up the router to connect to the modem wirelessly. This is useful for homes and offices where you need internet access across several devices.
Make sure to secure your network with strong passwords for added protection. It’s important that your modem and router are compatible and have the latest firmware installed for better network performance and security. This wireless connection is typically achieved using Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) or manual configuration through a web browser. Following these steps will help you set up a wireless router network at home or in your office, allowing you to connect your devices and enjoy the convenience of Wi-Fi connectivity.

Connecting Your Devices Through a Wireless Router
Connecting a router to a modem wirelessly offers a convenient way to share your internet connection across multiple devices in your home. While a traditional router connection involves cables, there are ways to achieve a wireless link for specific scenarios. Here’s how:
Understand the Limitations
Before we dive into the steps, it’s important to understand that modems are not designed to transmit wireless signals on their own. Here’s what you should know:
- Modem’s Role: A modem’s primary function is to connect your home to the internet service provider (ISP). It doesn’t have the hardware to create a Wi-Fi network.
- Router’s Role: A router is designed to create a wireless network and distribute the internet connection from your modem to your devices.
Methods for Wireless Connection
Here are two common methods for achieving a wireless connection between your router and modem:
1. Using a Wireless Bridge
- Compatibility: Ensure that your router supports wireless bridge mode (also known as repeater mode).
- Setup: Configure your router to act as a wireless bridge and connect it to your existing modem/router’s wireless network.
2. Router with Built-in Modem
- Combo unit: Invest in a router with a built-in modem. This eliminates the need for a separate modem.
- Considerations: Make sure the router/modem combo is compatible with your internet service provider.

Detailed Setup Guides
Here’s a breakdown of how to set up each of these methods:
Setting Up a Wireless Bridge
- Access Router Settings: Log in to your router’s web interface using its IP address.
- Locate Wireless Bridge Mode: Navigate to the wireless settings and enable wireless bridge or repeater mode.
- Connect to Existing Network: Choose your existing modem/router’s Wi-Fi network (SSID) and enter its password.
- Save Changes: Save your router’s settings and reboot if necessary.
Using a Modem/Router Combo
- Compatibility Check: Verify that the modem/router is compatible with your internet service provider.
- Connect to ISP: Connect the combo unit directly to your internet source (cable outlet, phone line, etc.).
- Configure Settings: Follow the device’s instructions to set up the internet and wireless network.

Important Considerations
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed | Wireless bridges can potentially reduce internet speed. |
| Placement | Optimal placement of the bridge is important for signal strength. |
| Compatibility | Verify that your router supports wireless bridge mode. |
Key Takeaways
- Setting up a wireless network involves configuring both modem and router.
- Compatibility and updated firmware are crucial for network performance.
- Wireless router connections can be made using WPS or web browser setups.
Setting Up the Wireless Router Connection
Setting up a wireless router to your modem requires careful attention to the equipment you use and the steps you follow. A successful setup will ensure a stable and secure Wi-Fi network in your home.
Identifying the Proper Equipment
To begin, confirm that you have a wireless router and a compatible modem. Check with your internet service provider if you’re unsure about the equipment. You will also need an Ethernet cable for the initial setup and a power source for both devices.
Connecting Your Router to the Modem
Power up your modem and router. Connect the modem to the WAN port of the router using the Ethernet cable. This physical connection is crucial even when setting up wireless access.
Configuring the Router Settings
Access the router’s settings by typing the default IP address into a web browser. Use the provided username and password to log in. Once in, update the firmware if needed and navigate to wireless settings to enable Wi-Fi.
Securing Your Wireless Network
Security is essential. Set up WPA2-PSK encryption for your network and choose a strong password. Change the default network name (SSID) to something unique and disable any features you don’t need, like remote administration.
Finalizing the Connection
After applying the settings, disconnect the Ethernet cable if you want to connect devices wirelessly. Test the connection by connecting a device to your Wi-Fi network. Make sure the location of your router maximizes signal strength throughout your home.
Troubleshooting Connection Issues
If devices struggle to connect, power off the router and power it on again. Check for signal issues and ensure the settings are correct. If problems persist, a reset might be necessary, but note that this will wipe all current settings.
Enhancing Network Performance
To get the most out of a wireless router connection to a modem, pay attention to network performance. It hinges on key factors including router placement, firmware updates, extending coverage, and secure network practices.
Optimizing Router Placement
Place your router in a central location away from interference and obstructions. Metal objects, walls, and other electronic devices can weaken the Wi-Fi signal. For optimal performance, the router should have a clear line of sight to the devices it connects.
Upgrading Firmware and Network Equipment
Keep your router’s firmware up to date to ensure compatibility with the latest technology and to enhance security. Upgrading to an n router, which supports a faster and more reliable Wi-Fi standard, might be necessary for older models.
Extending Wireless Coverage and Capacity
If your space is large and your router does not cover all areas, consider using a Wi-Fi extender or switch to repeater mode if your router supports it. This will increase the Wi-Fi coverage and allow for more multiple devices to connect without losing signal strength.
Maintaining Secure and Efficient Network
To maintain a secure network, change the default SSID and password provided by the service provider. Create separate guest networks for visitors to ensure they do not access the main network where your personal devices are connected. Use wired connections like Ethernet cables for desktop computers for more stability.
Setting Up Your Wireless Network: A Step-by-Step Guide
Gather Your Equipment
Before diving in, ensure you have the essentials:
- Broadband Internet Connection & Modem: This is your gateway to the internet. Your internet service provider (ISP) will supply this.
- Wireless Router: This device broadcasts the Wi-Fi signal, allowing your devices to connect wirelessly.
- Ethernet Cables: You’ll need these to connect the modem to the router and, optionally, to connect devices directly to the router for wired connections.
Modem and Internet Connection Setup
If your ISP hasn’t pre-configured your modem, refer to its instructions for connecting it to your computer and the internet. DSL modems connect to a phone jack, while cable modems connect to a cable jack. Ensure your computer detects an internet connection before proceeding.
Positioning Your Wireless Router
Strategic placement of your router optimizes signal strength and minimizes interference.
- Central Location: Place the router in a central, open area for even coverage.
- Elevated Position: Avoid placing it on the floor or near walls and metal objects.
- Reduce Interference: Keep it away from devices that use the 2.4 GHz frequency, such as microwaves and cordless phones. Consider a 5.8 GHz cordless phone to minimize disruptions.
Connecting the Router
Power on your devices in the correct order to ensure a smooth setup.
- Turn off the modem: Power down your modem first.
- Connect modem to router: Use an Ethernet cable to connect the modem’s LAN port to the router’s WAN/Internet port.
- Power on the modem: Turn on the modem and wait for it to boot up (a few minutes).
- Power on the router: Connect the power supply and turn on the router. Wait for it to boot up.
Configuration Using App or Web Interface
Many routers offer user-friendly mobile apps or web interfaces for easy configuration.
- Mobile App: If available, use the app provided by your router’s manufacturer. This often simplifies the setup process.
- Web Interface: If there’s no app, connect your computer to the router with an Ethernet cable. Access the router’s web interface by typing its IP address (often found on a sticker on the router or in its documentation) into your web browser’s address bar.
Crucial Configuration Steps
Secure your network and customize settings for optimal performance.
- Change default credentials: Create a strong, unique username and password for your router’s admin account.
- Update firmware: Check for and install any available firmware updates for your router.
- Set up Wi-Fi: Choose a network name (SSID) and a strong password (WPA3 security is recommended if supported).
- Configure security: Enable additional security features like firewalls and access controls if desired.
Connecting Devices
Once your router is configured, connect your devices.
- Wireless connection: Find your network name in your device’s Wi-Fi settings, enter the password, and connect.
- Wired connection: Use Ethernet cables to connect devices directly to the router’s LAN ports for a more stable connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
When setting up a home network, you might have some queries about connecting your wireless router to a modem. Here’s a selection of common questions and direct answers tailored to help you get the job done.
What are the steps for connecting a wireless router to a modem?
To connect a wireless router to a modem, power on both devices. Access the router’s admin page using its IP address in a browser. Choose the wireless setting and follow the onscreen prompts to establish a connection.
Is it possible to use a WiFi router without a direct Ethernet connection to the modem?
Yes, one can use WDS bridging or repeater mode to link a WiFi router to a modem without an Ethernet cable. Ensure both devices support this feature.
How can I set up my router with a modem/router combination unit?
For a modem/router combo, you’ll log into the admin interface typically via a web browser. Look for wireless bridging or repeating functions and activate this mode following the given instructions.
What is required to connect a wireless router to a Spectrum modem?
Connect a wireless router to a Spectrum modem by ensuring both devices are on. Find the IP on the router’s label, enter it in a browser, and follow steps to set it up via WiFi settings found in the admin area.
How can I access the settings of a router without using an Ethernet cable?
To access router settings wirelessly, connect your computer or smart device to the router’s network. Use the network’s IP address in a web browser and enter the login credentials.
Does a WiFi router require a physical connection to function with a modem?
A WiFi router typically needs a physical Ethernet link to a modem for internet access; however, alternative methods like WDS may allow a wireless connection if supported by the device’s firmware.
What is the difference between a cable-modem and a wifi router?
A cable modem connects a home network to an internet service provider (ISP), while a WiFi router distributes that internet connection to devices on the network.
- Cable modem: Translates signals from an ISP into a digital signal that devices can interpret. It’s responsible for sending and receiving signals from the ISP. However, modems don’t maintain data traffic, read the destination of data packets, or protect devices from cyber threats.
- WiFi router: Manages the flow of data within and between networks, and sends information from the internet to devices like computers, phones, and tablets. It allows devices to connect wirelessly via WiFi or through Ethernet cables, and also lets them communicate with each other directly. However, a router can reduce connection speeds between devices and the modem, which can lead to a slow internet experience. To improve coverage and speed, or take advantage of the latest WiFi technology, routers may need to be updated every year or two