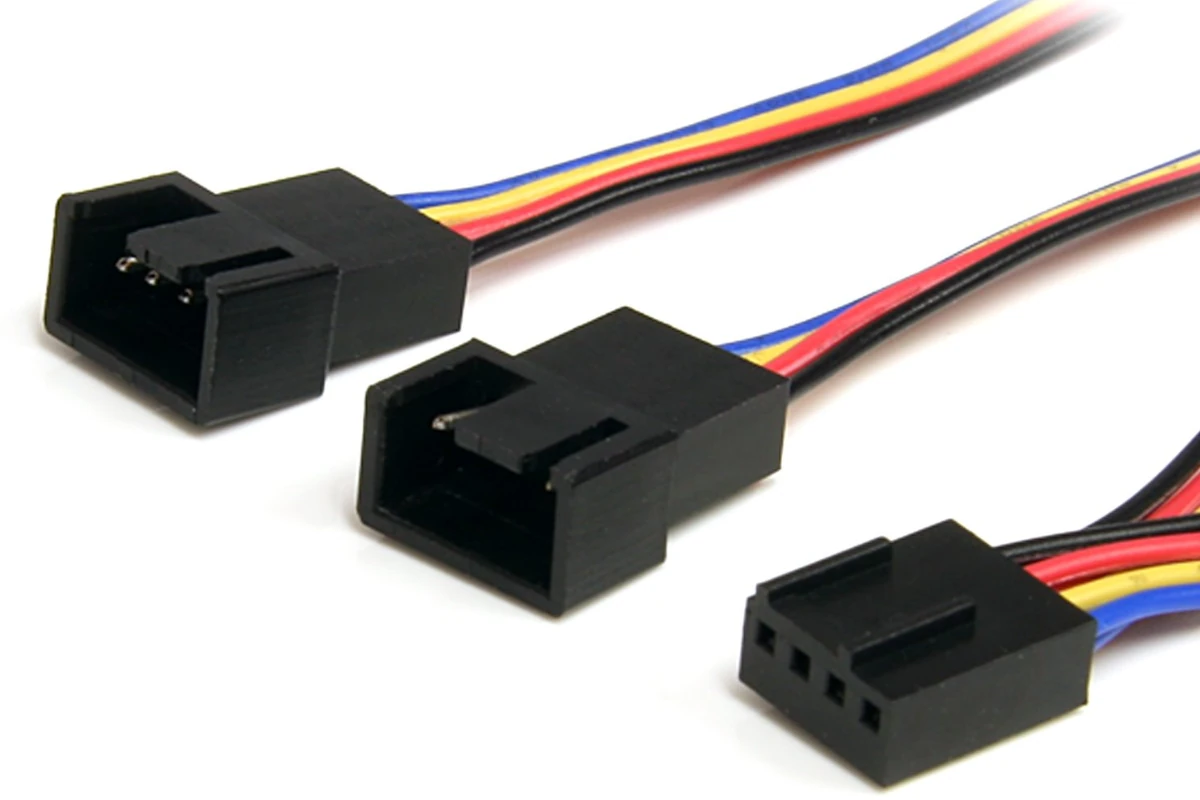
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) cables are crucial for controlling the speed of fans and pumps in electronic devices. These cables allow devices to adjust their cooling speed dynamically by regulating the voltage supplied to the fan motor. This results in more accurate cooling responses to temperature changes inside the device, leading to efficient thermal management and reduced noise levels.
PWM cables typically include a 4-pin connector, which differs from the traditional 3-pin fan connector by an additional pin for controlling fan speeds. It’s important to connect these cables to the motherboard’s 4-pin headers, which are usually labeled with names like “CPU_FAN” or “SYS_FAN.” Properly connecting the PWM cables to the right headers on the motherboard is crucial for the devices’ thermal performance. This can be done by following the motherboard’s manual or seeking advice from online forums if the labeling on the motherboard is unclear.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Pulse Width Modulation Cable |
| What it Does | Carries a signal to control fan speed |
| How it Works | Uses a series of on-off pulses to regulate power delivered to a fan |
| Benefits | – Precise control over fan speeds |
| Connection | Typically a 4-pin connector |
| Plugs into | A 4-pin header on the motherboard labeled “CPU_FAN” or “SYS_FAN” |
Key Takeaways
- PWM cables regulate fan speed and motor voltage for efficient cooling.
- These cables have a 4-pin design, distinct from standard 3-pin connectors.
- Correctly connecting to motherboard headers is critical for optimal performance.
Understanding PWM Cables
PWM cables are a critical component for managing the performance of cooling fans in computers and other devices. These cables help to regulate fan speed with precision.
Basics of Pulse Width Modulation
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a technique used to control the amount of power delivered to an electrical device. In the case of cooling fans, PWM signals adjust the speed at which the fan blades spin. This translates to better energy efficiency and noise control. The key to PWM is its ability to maintain a constant voltage while modulating the width of the power pulses.
Types of PWM Cables
There are two main types of connectors for PWM cables: the three-pin headers and the four-pin headers.
Three-pin headers:
- Power
- Ground
- Tachometer signal
Four-pin headers:
- Power
- Ground
- Tachometer signal
- PWM signal
The four-pin PWM cable allows for more sophisticated control and is typically used with 4-pin connectors on motherboards. A 3-pin connector can still be used for fans with simpler needs and doesn’t require the same level of control.
PWM Cable Integration
Integrating PWM cables correctly into a computer system is vital for efficient cooling and noise management.
Configuring Motherboard Headers
Motherboards usually feature several fan headers including CPU_FAN, SYS_FAN, CHA_FAN, and sometimes PWR_FAN or EXT_FAN. To enable precise control over fan speeds, connect your PWM fans to headers labeled with PWM or those specifying a 4-pin configuration. These pins provide a PWM signal essential for regulating fan speed. Should you need to check the exact locations and configurations, refer to your motherboard’s manual.
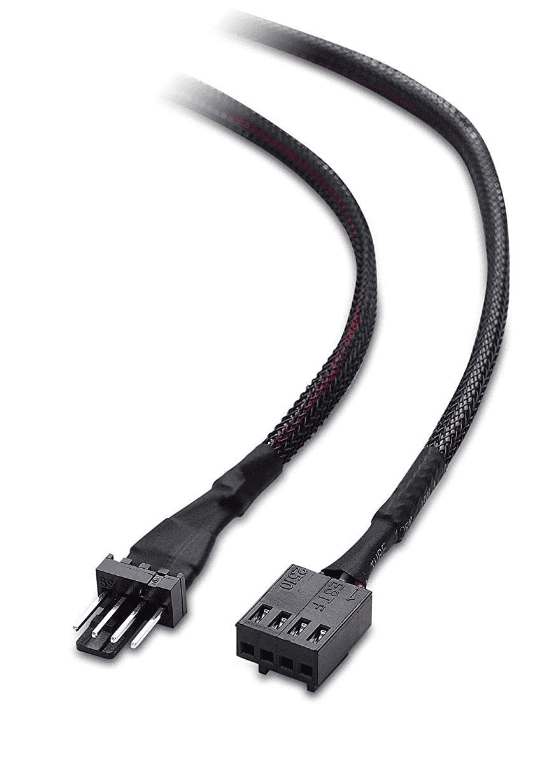

Connecting Different Fan Types
There are two main types of fans used in computers: PWM fans and DC (or regular) fans. PWM fans have 4-pin connectors and allow for more accurate speed control; connect these to 4-pin headers on your motherboard. Ensure the tab on the connector aligns with the guide on the motherboard header to avoid damage. DC fans use a 3-pin connector and can be connected to either 3-pin or 4-pin headers, but with less precise control.
Managing Fan Speed and Noise
Balancing cooling performance with a quiet environment involves managing fan speeds. Most motherboards come with a Smart Fan Mode in the BIOS settings that automatically adjusts the fan speeds based on temperature readings. For manual control, fan controller software or hardware can grant you command over individual fans. When connecting multiple fans, splitters, Y-splitters, or hubs can be employed but consider the total amperage to prevent overloading the header. Extensive use of these might necessitate extensions or additional power sources to manage the load effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
This part of the article addresses common inquiries about PWM cables, focusing on how they operate and how they can be utilized effectively in various computer setups.
What is the purpose of a 4-pin PWM cable?
A 4-pin PWM cable enables precise control over fan speeds. This cable allows the motherboard to adjust the fan’s power, regulating its speed without altering the power supply voltage.
How do you connect a PWM cable to a motherboard?
To connect a PWM cable to a motherboard, locate the 4-pin headers usually labeled as “CPU_FAN,” “SYS_FAN,” or a similar term. Align the cable’s connector with the header and gently insert it to establish the connection.
Can you control multiple PWM fans with a single controller?
Yes, multiple PWM fans can be managed by a single controller. This is often done using a fan hub or splitter cable that connects several fans to one PWM signal from the motherboard.
What is the difference between 3-pin and 4-pin fan cables?
The primary difference is control. A 3-pin cable supplies constant voltage and lacks the ability to regulate fan speed. The 4-pin cable, with its additional pin, supports PWM signals allowing dynamic speed adjustment.
How do you use a PWM controller in a dual fan setup?
In a dual fan setup, connect each fan to the PWM controller using a Y-splitter or by plugging them into designated ports if the controller has multiple outputs. Then, connect the controller to the PWM header on the motherboard.
Where do you connect PWM cables in a Corsair case?
For a Corsair case, identify the PWM headers on the motherboard, which are typically located near the CPU socket. Connect the PWM cables from the case fans to these headers, ensuring they are matched correctly with the 4-pin configuration.