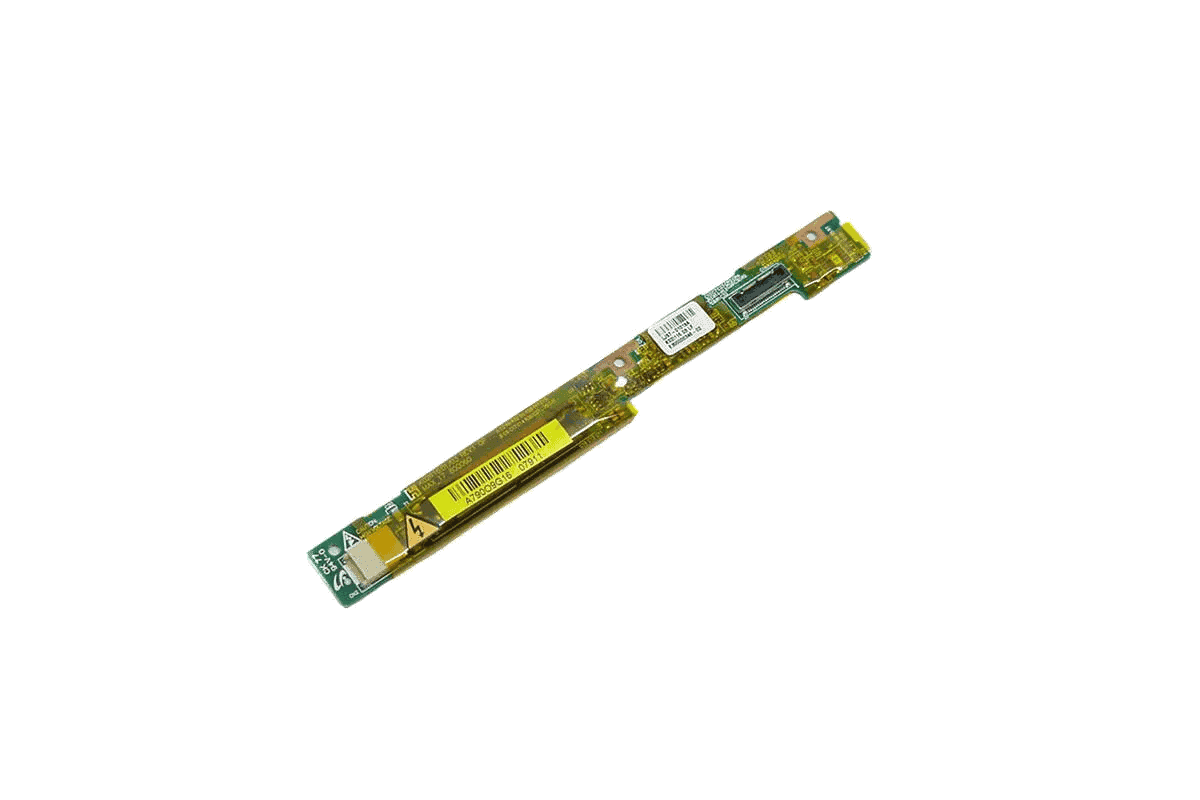
The LCD inverter is an essential part of many laptops, monitors, and LCD screens. It helps power the screen’s backlight by converting the direct current (DC) from the laptop into the alternating current (AC) needed by the backlight. Without the inverter, the screen would remain dark.The inverter is usually located near the screen, and its main job is to make sure that the backlight of the LCD screen lights up, allowing you to see images. Even as technology changes, the fundamental role of the inverter remains the same.
Understanding the LCD inverter can give insight into how display screens work. This article explores how LCD inverters function, the different types of LCD backlights they power, and common issues that can occur. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just curious about how your devices work, learning about the LCD inverter is a gateway to understanding display technology.
The LCD Inverter’s Role in Display Illumination
An LCD inverter is a small electronic device that plays a crucial role in how LCD screens work. LCDs, or liquid crystal displays, are found in everything from TVs and computer monitors to smartphones and tablets.
How Does an LCD Inverter Work?
In simple terms, an LCD inverter takes the direct current (DC) power from the device’s battery or power supply and converts it into the alternating current (AC) power needed to light up the screen’s backlight. This backlight is what allows you to see the images on the LCD panel.
Different Types of LCD Backlights
There are two main types of LCD backlights that use inverters:
- Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp (CCFL): This older technology uses fluorescent tubes to produce light. CCFL backlights require high voltages to operate, which is why they need an inverter.
- Light Emitting Diode (LED): This newer technology uses LEDs to produce light. While some LED backlights can run on DC power, others still require an inverter to control the brightness and dimming of the LEDs.
Common Issues with LCD Inverters
Like any electronic component, LCD inverters can sometimes fail. Common signs of a failing inverter include:
- Dim screen: If the screen is noticeably dimmer than usual, it could be due to a failing inverter.
- Flickering screen: A flickering screen can also be a sign of a failing inverter.
- No display: In some cases, a completely dead screen could be caused by a faulty inverter.
Troubleshooting and Repairing LCD Inverters
Disclaimer:
- Working with electronics and high voltage can be dangerous. Proceed with caution and only attempt repairs if you have the necessary skills and knowledge.
- If you are unsure, consult a qualified technician.
Safety First:
- Unplug the device: Always disconnect the power source before beginning any repairs.
- Discharge capacitors: High voltage capacitors can retain a charge even after the device is unplugged. Discharge them safely using a high-voltage resistor.
- Wear protective gear: Use safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from electrical shock and sharp objects.
- Work in a well-ventilated area: Solder fumes can be harmful, so ensure proper ventilation.
Troubleshooting and Repair Steps:
Identify the problem:
- No backlight: This is the most common symptom of a faulty inverter. The screen may be dim or completely black, but you might still be able to see an image if you shine a flashlight on it.
- Flickering backlight: The backlight may flicker or turn on and off intermittently.
- Dim backlight: The backlight may be dimmer than usual.
Disassemble the device:
- Carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions or online guides for your specific device model.
- Take note of the screws and cable connections to ensure proper reassembly.
Locate the inverter:
- The inverter is usually a small circuit board with high-voltage wires connected to the backlight lamps.
- It may be located near the power supply or along the edge of the screen.
Inspect the inverter:
- Look for visible damage such as burnt components, cracked solder joints, or swollen capacitors.
- Use a multimeter to test the components for continuity and proper voltage levels.
Replace faulty components:
- If you find damaged components, replace them with compatible parts.
- Be sure to use the correct soldering techniques to avoid further damage.
Reassemble the device:
- Carefully reconnect all cables and screws.
- Double-check your work before plugging in the device.
Test the device:
- Plug in the device and turn it on.
- If the backlight works correctly, congratulations! You have successfully repaired the inverter.
- If the problem persists, you may need to consult a technician or consider replacing the entire inverter board.
Additional Tips:
- Use the correct tools: Having the right tools for the job will make the repair process easier and safer.
- Take your time: Rushing can lead to mistakes and further damage. Be patient and methodical.
- Document your work: Take pictures or notes as you go to help with reassembly.
- Research online: Many online resources and forums can provide additional guidance and troubleshooting tips.
- Know your limits: If you are unsure about a step or encounter a complex issue, seek professional help.
Remember, attempting repairs yourself can void the warranty on your device. Proceed at your own risk and prioritize safety at all times.
Alternative Resources:
- You can find detailed repair guides and videos on platforms like YouTube and iFixit.
- Consider purchasing an inverter repair kit specifically designed for your device model.
If you suspect your LCD inverter is faulty, there are a few things you can try:
- Check the power connections: Make sure the inverter is properly connected to the power source and the LCD panel.
- Test the inverter: You can use a multimeter to test the inverter’s output voltage.
- Replace the inverter: If the inverter is indeed faulty, it will need to be replaced. This is usually a job for a qualified technician.
The Future of LCD Inverters
While LCD inverters are still widely used in many displays, their future is somewhat uncertain. As LED backlights become more efficient and affordable, the need for inverters may decrease. However, for the foreseeable future, LCD inverters will continue to play an important role in display technology.
Table: LCD Inverter vs. LED Driver
| Feature | LCD Inverter | LED Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Power Input | DC | DC |
| Power Output | AC | DC |
| Backlight Type | CCFL, some LED | LED |
| Voltage Output | High | Low |
| Common Issues | Dimming, flickering, no display | Flickering, dimming |
| Replacement | Often requires a technician | DIY possible in some cases |
Key Takeaways
- LCD inverters convert DC power from the computer to AC power for the backlight.
- The inverter is crucial for the visibility of the screen’s display.
- Issues with the inverter can cause the display to remain dim or completely dark.
Understanding LCD Inverters
LCD inverters play a critical role in screen display technology, transforming power types and illuminating screens.
Inverter Function and Importance
Inverters are essential for an LCD screen as they convert DC (Direct Current) from the power supply to AC (Alternating Current), enabling the backlight to function. Without an inverter, the screen would remain dim and unusable because the backlight is what makes the display visible.
Components of an LCD Inverter
An inverter board typically includes a circuit with several key components such as transistors, resistors, capacitors, and sometimes a fuse. These components work together to manage the flow of electricity and generate the necessary voltage to power the screen’s backlight.
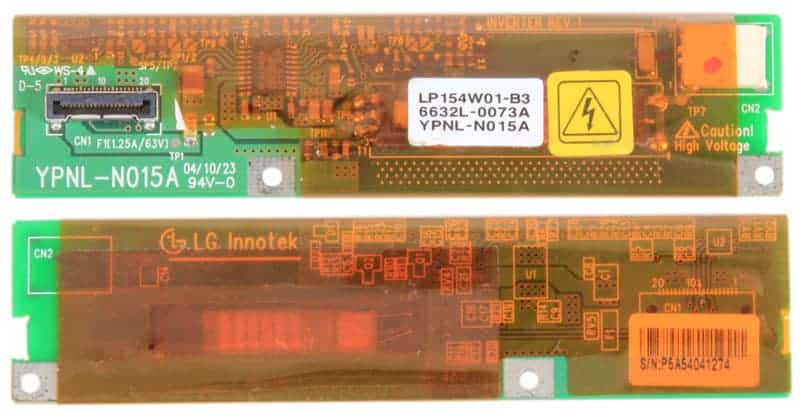
Types of LCD Inverters
There are mainly two types of inverters found in LCD displays:
- CCFL Inverters, which power cold-cathode fluorescent lamp backlights, commonly found in older screens.
- LED Inverters, which are used for modern screens with LED backlights, though these are often less complex thanks to the nature of LED lighting.
Troubleshooting and Repair
When an LCD inverter is failing, the screen’s backlight may flicker, lose brightness, or stop working entirely. With the right approach, you can often identify and even fix these issues yourself. Here’s how to address problems with your monitor or laptop’s LCD inverter efficiently.
Identifying Inverter Failure
A failing LCD inverter often presents clear signs before complete failure. Flickering or dim screen conditions are common indicators. Specifically, a dim screen can imply that the inverter is no longer able to convert DC power to the necessary AC power to maintain backlight consistency. To ascertain this, turn on your monitor or laptop in a darkened room. If the screen briefly lights up and then goes dark again or has an inconsistent glow, it may be the inverter’s wiring or the circuit board that’s in trouble.
Repairing an Inverter
Repairing an LCD inverter involves a few careful steps. After ensuring the power source to your device is off, you’ll need a screwdriver to open up the panel, usually located at the bottom edge or the corner of the screen. Typical tools for this job include cross-head or flat-head screwdrivers, depending on the types of screws used. Once inside, you can check for loose wires or broken components on the inverter board. Soldering may be required to reattach wires or to replace components that are visibly damaged.

Replacing an LCD Inverter
Should troubleshooting and repair attempts not yield results, replacing the inverter could be the necessary course of action. Most laptops or monitors have model-specific inverters, so ensure you have the correct replacement part for your model, which might be specific to brands like Dell. With the replacement inverter ready, remove the old one by disconnecting its wires and unscrewing it from the motherboard or frame. Install the new inverter by reversing these steps, reattach all connectors securely, then test the device to confirm the backlight is consistently working.
Frequently Asked Questions
In exploring the pivotal role of an LCD inverter, it’s essential to shed light on some of the common queries people have about this component. From its basic operation to troubleshooting tips, let’s dig into the specifics.
How does an LCD inverter function in a laptop?
An LCD inverter in a laptop is responsible for converting the DC power from the battery to AC power, which is necessary to illuminate the screen’s backlight. This conversion is vital for the visibility of the display under various lighting conditions.

What are common symptoms of LCD inverter failure?
When an LCD inverter starts failing, one might notice the laptop screen becoming dim, flickering, or occasionally going black. These symptoms indicate that the inverter is unable to maintain a stable power supply to the backlight.
Which displays require the use of an inverter?
Displays that use cold-cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs) as a backlight source require an inverter. Modern LCD screens often use LED backlights that usually don’t need an inverter.
What role does an inverter play in a monitor’s operation?
The inverter’s role in a monitor is akin to that in a laptop; it supplies the AC power needed for the backlight. This continuous power stream is what makes images on the monitor visible to users.
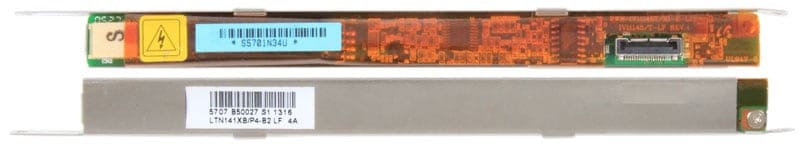
How can one diagnose issues with a laptop’s LCD inverter?
Troubleshooting an inverter involves checking the display for any signs of life, like faint images or brightness changes. If the screen is entirely dark but the laptop seems to be working, it might be an inverter issue.
What are the distinguishing characteristics of a laptop LCD inverter circuit?
A laptop’s LCD inverter circuit is distinct because it’s typically a small, elongated board located near the display panel. It is designed to be efficient, converting power with minimal energy loss, crucial for battery-powered devices.