When a computer encounters a problem starting up, having the proper tools to fix the issue is crucial. In cases where the required installation media such as a USB or DVD is not available, Windows offers built-in recovery tools that can help resolve startup problems. Knowing how to access and use these tools is essential for troubleshooting and getting your system up and running again without the need for external media.
Recovery tools are integrated into Windows to address boot issues and system errors that may prevent normal operation. These tools include features like Startup Repair, which can automatically fix problems that prevent Windows from starting. For more persistent issues, the Command Prompt provides advanced troubleshooting commands like ‘chkdsk’ to check the disk for errors. Using these tools effectively can save users time and avoid the hassle of finding or creating installation media.
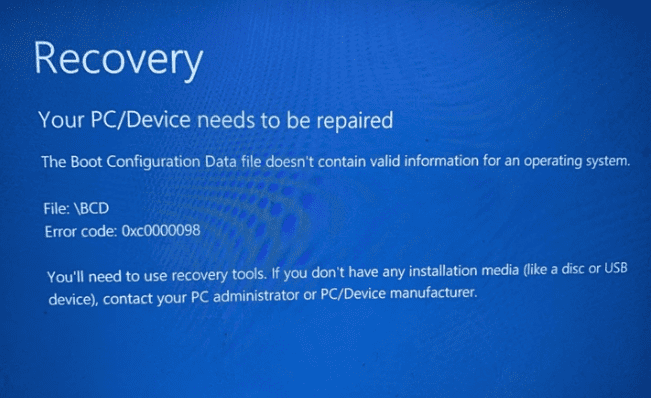
The text of the error is usually something along the lines of:
Error code 0xc0000098: You’ll need to use recovery tools if you don’t have any installation media (like a disc or USB device), contact your PC administrator or PC/Device manufacturer.
What To Do When You Get the Error Message
When your Windows computer suddenly won’t boot, you might encounter the error message: “You’ll need to use recovery tools. If you don’t have any installation media (like a disc or USB device), contact your PC administrator or PC/device manufacturer.” This can be frustrating, but there’s no need to panic.
Here’s a breakdown of what this error means and how you can restore your system.
Understanding the Error Message
This error usually occurs when Windows encounters severe corruption in its system files or the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) store. This missing or corrupt information makes it impossible to load the operating system.
Possible reasons for system corruption are:
- Hard drive issues: Problems with your hard drive can damage important system files.
- Malware or virus infection: Viruses and other malware can damage or delete vital system components.
- Power failures: Sudden power outages during operating system updates or core file changes could cause corruption.
- Accidentally deleted system files: Critical system files can occasionally get unintentionally deleted.
What are Recovery Tools?
Recovery tools are built-in utilities within Windows designed for fixing problems that prevent the operating system from starting. You’ll typically find these tools within the Windows Recovery Environment.
How to Access the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE)
- Force shutdown: Press and hold your computer’s power button to shut it down. Repeat this process three times to automatically trigger the WinRE.
- Advanced Startup options: If your system can still partially boot, access the ‘Settings’ app, go to “Update & Security,” click on “Recovery,” and then select “Restart now” under “Advanced Startup.”
Recovery Tools Within WinRE
Here’s a breakdown of the tools within WinRE you can use to troubleshoot and restore your system:
| Recovery Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Startup Repair | Automatically scans for and attempts to fix problems that prevent Windows from loading. |
| System Restore | Restores your Windows system to an earlier point in time using Restore Points. (You must have created Restore Points beforehand for this to work). |
| System Image Recovery | Allows you to restore your entire system with a previously created system image backup. |
| Command Prompt | Opens a command line interface for advanced troubleshooting tasks like rebuilding the BCD or checking disk integrity. |
| Go back to the previous version | Rolls back to an earlier build of Windows if a recent update caused problems. |
Note: To troubleshoot your system without installation media, you’ll primarily rely on Startup Repair, System Restore, or advanced Command Prompt commands.
Key Takeaways
- Built-in recovery tools can address startup issues without installation media.
- Startup Repair and Command Prompt are essential for system troubleshooting.
- Effective use of these tools can streamline the recovery process.
Preparing for Recovery
When your PC runs into trouble and you don’t have installation media, proper preparation can make the recovery process smoother. The steps outlined here will guide you through accessing your computer’s settings, creating a recovery tool, and understanding your device’s specifications.
Accessing UEFI Firmware Settings
To modify your PC’s basic operations, you may need to enter the UEFI Firmware Settings. Turn your PC on and off three times to perform a hard reboot, which should open the automatic repair screen. From here, choose ‘Troubleshoot’ and then ‘Advanced options’. Select ‘UEFI Firmware Settings’ to make any necessary changes, such as enabling a USB device to start your PC.
Creating Recovery Drive
A recovery drive is a must-have for PC repair. To create one, you’ll need a USB flash drive with enough space. Connect this USB to your PC. Search for ‘Create a recovery drive’ in the Windows search bar and follow the on-screen steps. Make sure to tick the option to ‘Back up system files to the recovery drive’. This will make your USB drive a valuable tool if you face system issues.
Identifying Your System Specs
Knowing your PC’s hardware like the type of SSD or memory it uses can help during recovery. Press ‘Windows Key + X’ and select ‘System’. Take note of the processor, installed RAM, and other information under ‘Device specifications’. This info is helpful if you need to talk to a PC administrator or when searching for compatible recovery tools and drivers.
Executing Recovery Processes
When a system faces issues booting or malfunctioning due to system errors or corruption, recovery processes become essential. They are designed to resolve software problems that prevent the computer from running normally.
Using System Restore
System Restore helps to roll back the computer’s state to a previous point in time. This can fix problems caused by a recent change to the system. To use System Restore:
- Open the Start menu.
- Type ‘Create a restore point’ and hit Enter.
- In the System Properties window, click ‘System Restore’.
- Follow the prompts to select a restore point and begin the restoration process.
Resetting Your PC
Resetting your PC reinstalls Windows but gives you the option to keep your files. Here’s how to reset your PC:
- Go to Settings.
- Click on ‘Update & Security’.
- Choose ‘Recovery’ and then ‘Get started’ under Reset this PC.
- Select ‘Keep my files’ or ‘Remove everything’ and follow the instructions.
Rebuilding Boot Configuration Data
Boot Configuration Data (BCD) is vital for the boot process. To fix BCD problems using the command prompt:
- Boot from installation media and choose ‘Troubleshoot’.
- Open ‘Command Prompt’.
- Type ‘bootrec /rebuildbcd’ and press Enter.
- Follow the steps to rebuild the BCD.
Troubleshooting with Advanced Options
If you encounter a blue screen or Windows fails to start, Advanced Options can help. To access them without installation media:
- Hold the power button to interrupt the boot process three times.
- This will enter the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE).
- Click ‘Troubleshoot’ and then ‘Advanced options’.
- Now you can select Startup Repair, Command Prompt for manual repairs, or Startup Settings to boot in Safe Mode.
With these tools, users can address a variety of issues such as blue screen errors, missing or corrupt system files, and boot problems, even without installation media. Each step above provides a path to recovery, aiming to restore system functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions
When dealing with PC startup errors without installation media, recovery tools are crucial. This section addresses common issues and provides clear solutions.
How can I fix the ‘Your PC needs to be repaired’ error on Windows 10?
To resolve this error, restart your PC using the installation DVD or USB. Boot from it, select ‘Troubleshooting’, then ‘Advanced Options’, and finally ‘Startup Repair’.
What should I do when I receive error code 0xc00000e or 0xc00000f during startup?
Errors 0xc00000e and 0xc00000f suggest a hardware problem or a missing boot file. Running a repair with the Windows installation media can help. If you don’t have it, you can use Command Prompt to run commands like ‘chkdsk /f’ to fix file system errors.
Why does my PC display ‘Your PC needs to be repaired’ when booting from USB?
This message may appear if the USB is not properly created as a bootable device or your PC’s BIOS settings are not configured to boot from USB. Ensure the bootable USB is made correctly and check your BIOS settings.
How do I access and use Windows recovery tools to repair my PC?
Access Windows recovery tools through your PC’s built-in recovery partition or by using Windows installation media. Once accessed, you can use options like System Restore, Automatic Repair, or Reset this PC.
Why is my device indicating that a required device isn’t connected or can’t be accessed during boot?
This error often means your system can’t find the necessary hardware to boot. Check connections for your hard drive or any other bootable devices. It could also mean the BIOS does not recognize the device, requiring you to check the BIOS settings.
What steps should I take if my PC reports that the kernel is missing or corrupt?
A missing or corrupt kernel indicates system file issues. Use the System File Checker tool by opening Command Prompt and typing ‘sfc /scannow’. This will scan and repair missing or corrupted system files.