Processor speed is a key factor in computer performance. It determines how quickly your CPU can execute tasks and run programs. Clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), indicates how many cycles a CPU can perform per second.
But raw clock speed isn’t the only measure of CPU performance. Modern processors have multiple cores and threads. These allow them to handle several tasks at once. Other factors like cache size and architecture also play a role in overall speed.
To truly gauge processor speed, benchmarking tools are useful. These run standardized tests to compare different CPUs. They provide scores that reflect real-world performance across various tasks. This gives a more complete picture of a processor’s capabilities beyond just its GHz rating.

Unleash the Need for Speed: Measuring Your Processor’s Performance
Curious about how fast your computer’s processor really is? Whether you’re a gamer, a creative professional, or just want to know what your hardware is capable of, measuring your processor speed can give you valuable insights. Here’s a breakdown of the methods and software you can use to put your CPU to the test.
Understanding Processor Speed
Before we dive in, let’s clarify what we mean by “processor speed.” It’s usually measured in gigahertz (GHz), which represents how many clock cycles your CPU can execute per second. However, a higher GHz doesn’t always mean a faster processor. Other factors like the number of cores, cache size, and architecture also play a significant role in overall performance.
Methods to Measure Processor Speed
There are two main approaches to measuring processor speed:
- Benchmarking Software: This software runs a series of standardized tests designed to push your processor to its limits. It then provides a score or rating that you can compare to other processors.
- Task Manager/System Information: Your operating system provides tools that display your processor’s base clock speed and current usage. While this doesn’t give you a comprehensive performance analysis, it’s a quick way to see basic information.
Popular Benchmarking Software
- Cinebench: A popular and reliable tool that tests CPU performance using real-world rendering tasks.
- Geekbench: A cross-platform benchmark that measures both single-core and multi-core performance.
- 3DMark: Primarily known for graphics card testing, but also includes CPU benchmarks relevant for gaming performance.
- PCMark: Focuses on overall system performance, including tests that evaluate CPU performance in everyday tasks like web browsing and video editing.
Using Task Manager/System Information
For a quick check of your processor speed:
- Windows: Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc), go to the “Performance” tab, and select “CPU.” You’ll see your processor’s base speed and current utilization.
- macOS: Go to “About This Mac” and click on “System Report.” Under the “Hardware” section, select “Processor” to view details about your CPU, including its speed.
Interpreting the Results
Benchmarking scores can be helpful for comparing different processors or seeing how your CPU performs relative to others. However, it’s important to remember that these are synthetic tests. Real-world performance can vary depending on the specific tasks and applications you use.
Factors Affecting Processor Speed
Keep in mind that several factors can influence your processor’s performance:
- Temperature: Overheating can cause your CPU to throttle its speed to prevent damage.
- Background Processes: Running multiple applications simultaneously can consume CPU resources and affect performance.
- Power Settings: Power saving modes can limit CPU performance to conserve energy.
Pros and Cons
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benchmarking Software | Runs standardized tests to measure CPU performance. | Provides detailed performance analysis and comparison data. | Scores may not perfectly reflect real-world performance. |
| Task Manager/System Information | Displays basic CPU information like clock speed and usage. | Quick and easy way to check basic CPU details. | Doesn’t provide in-depth performance analysis. |
Key Takeaways
- Clock speed in GHz is the basic measure of processor speed
- Multiple cores and threads allow CPUs to handle several tasks at once
- Benchmarking tools provide a comprehensive view of real-world CPU performance
Understanding Processor Speed and Its Importance
Processor speed plays a key role in computer performance. It affects how quickly tasks are completed and how smoothly programs run. Let’s explore the main factors that influence processor speed and why it matters.
Clock Speed and Performance
Clock speed is measured in gigahertz (GHz). It shows how many cycles a CPU can do per second. A higher clock speed usually means faster performance.
For example, a 3.5 GHz processor can do 3.5 billion cycles each second. This speed affects how fast the CPU can handle instructions.
But clock speed isn’t everything. Other factors like chip design also impact performance. Modern CPUs use tricks to boost speed beyond just clock rate.
Multi-Core Processors and Parallel Processing
Multi-core processors have several processing units on one chip. They can handle multiple tasks at once.
A quad-core CPU has four cores. An octa-core has eight. More cores often mean better performance for complex tasks.
Multi-core CPUs excel at multitasking. They can run several programs smoothly at the same time. This boosts overall system speed and responsiveness.
Impact on Task Efficiency
Processor speed greatly affects how fast tasks are completed. A faster CPU can crunch numbers and process data more quickly.
For basic tasks like web browsing, a mid-range processor is often enough. But for demanding jobs like video editing, a faster CPU makes a big difference.
Gaming performance also depends on CPU speed. Many games benefit from high clock speeds and multiple cores.
Faster processors can boost productivity. They reduce wait times and allow for smoother multitasking. This can lead to more efficient workflows.
Measuring and Testing CPU Performance
Measuring processor speed involves various tools and techniques. These methods help users understand their CPU’s capabilities and performance under different conditions.
Benchmarking Tools and Comparison
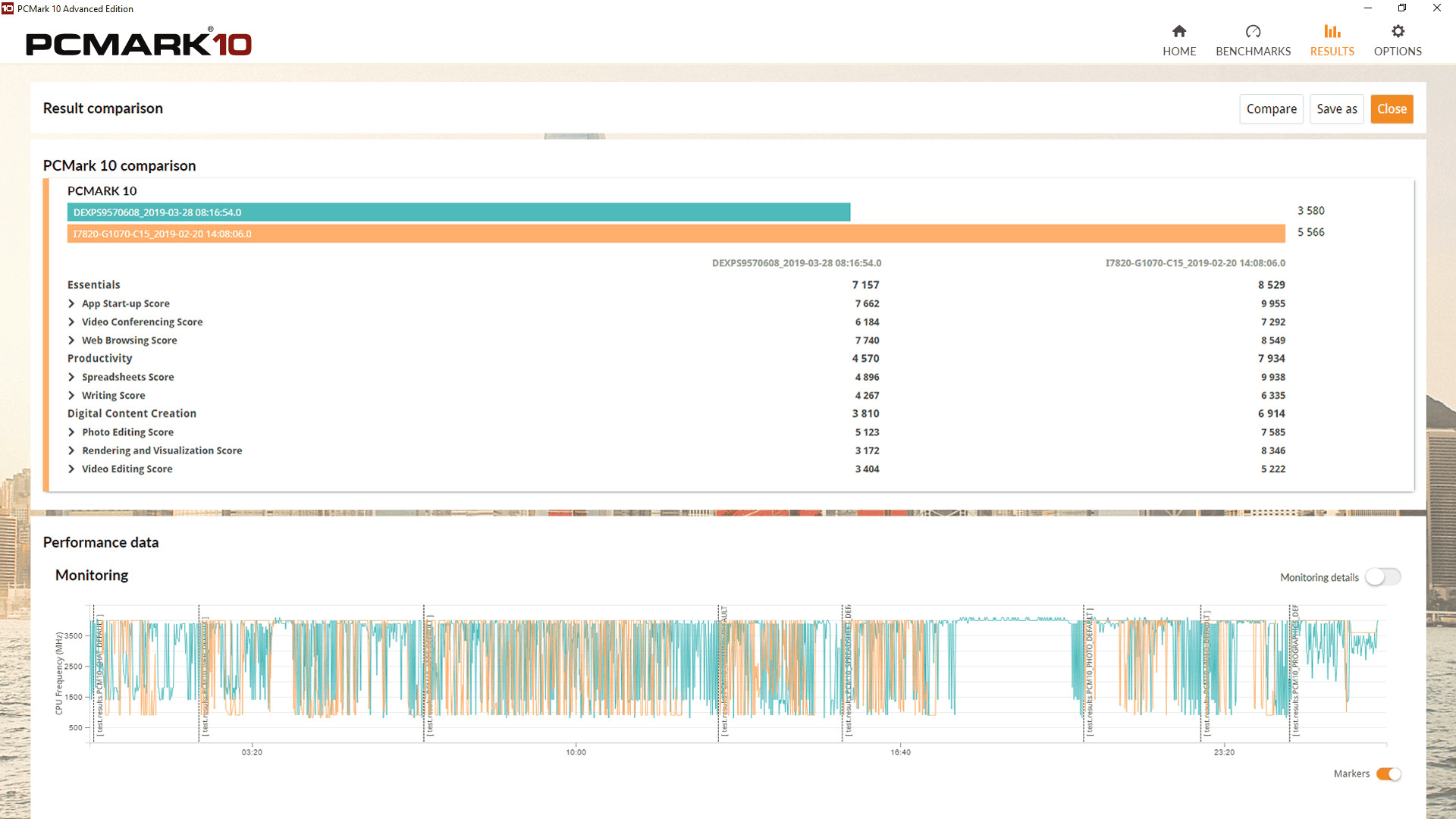
CPU benchmark tools are essential for testing processor performance. Popular options include PCMark 10, Cinebench, and PassMark. These programs run tests to evaluate CPU speed and power.
PCMark 10 simulates real-world tasks. It checks how well a CPU handles everyday activities. Cinebench focuses on 3D rendering. It tests single-core and multi-core performance. PassMark runs a series of CPU tests. It gives an overall score for easy comparison.
Users can compare their results with others online. This helps them see how their CPU stacks up against different models.
Analyzing Processor Workloads
Understanding CPU workloads is key to measuring performance. Different tasks stress the processor in unique ways.
Single-threaded tasks use one core heavily. Examples include some older games and basic web browsing. Multi-threaded tasks spread work across cores. Video editing and 3D rendering fall into this category.
Stress tests push the CPU to its limits. They help check stability and cooling performance. Prime95 is a popular tool for this purpose.
Monitoring tools like CPU-Z show real-time CPU usage and clock speeds. This data helps users see how their processor performs under various loads.
Utilizing Built-In System Tools
Windows 10 offers built-in tools to check CPU performance. These are easy to use and don’t require extra downloads.
Task Manager is a quick way to view CPU usage. Open it by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc. The Performance tab shows current CPU speed and usage.
System Information provides more details. Type “msinfo32” in the Start menu to open it. It displays the processor name and base speed.
For a simple CPU speed check, users can run a quick test. Open Command Prompt and type “wmic cpu get name, maxclockspeed”. This shows the CPU model and max speed in MHz.
Frequently Asked Questions
CPU speed measurement involves various methods and benchmarks. Different tools help check processing speed on different systems. Clock speed and other factors impact overall performance.
What methods are used to measure a CPU’s performance in gaming?
Gaming CPU performance is often measured by frame rates. Frames per second (FPS) shows how smoothly games run. Higher FPS means better performance.
Benchmarking software like 3DMark tests CPUs in gaming scenarios. These tools provide scores to compare different processors.
How can one determine the processing speed of a laptop’s CPU?
You can check a laptop’s CPU speed in the system information. On Windows press Windows key + I then go to System > About.
For Macs click the Apple menu then select About This Mac. The processor info will show the base clock speed.
What benchmarks indicate a fast processing speed for computers?
Cinebench tests 3D rendering speed. It gives a score that shows CPU power.
Geekbench measures both single-core and multi-core performance. Higher scores mean faster processing.
PassMark CPU Mark rates overall CPU speed. It compares processors across different brands and models.
What steps are involved in checking a CPU’s speed in Windows 10?
- Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc
- Click on the Performance tab
- Select CPU from the left menu
- The current clock speed will be shown on the right
You can also use third-party tools like CPU-Z for more detailed info.
What does MIPS mean in the context of a computer’s processing speed?
MIPS stands for Million Instructions Per Second. It measures how many operations a CPU can do in one second.
Higher MIPS values typically mean faster processing. But it’s not always a perfect measure of real-world performance.
How is CPU clock speed significant in computer performance?
Clock speed affects how fast a CPU can process instructions. It’s measured in gigahertz (GHz).
Higher clock speeds often mean faster performance. But other factors like core count and architecture also play big roles.
Modern CPUs can boost their clock speeds when needed for demanding tasks.