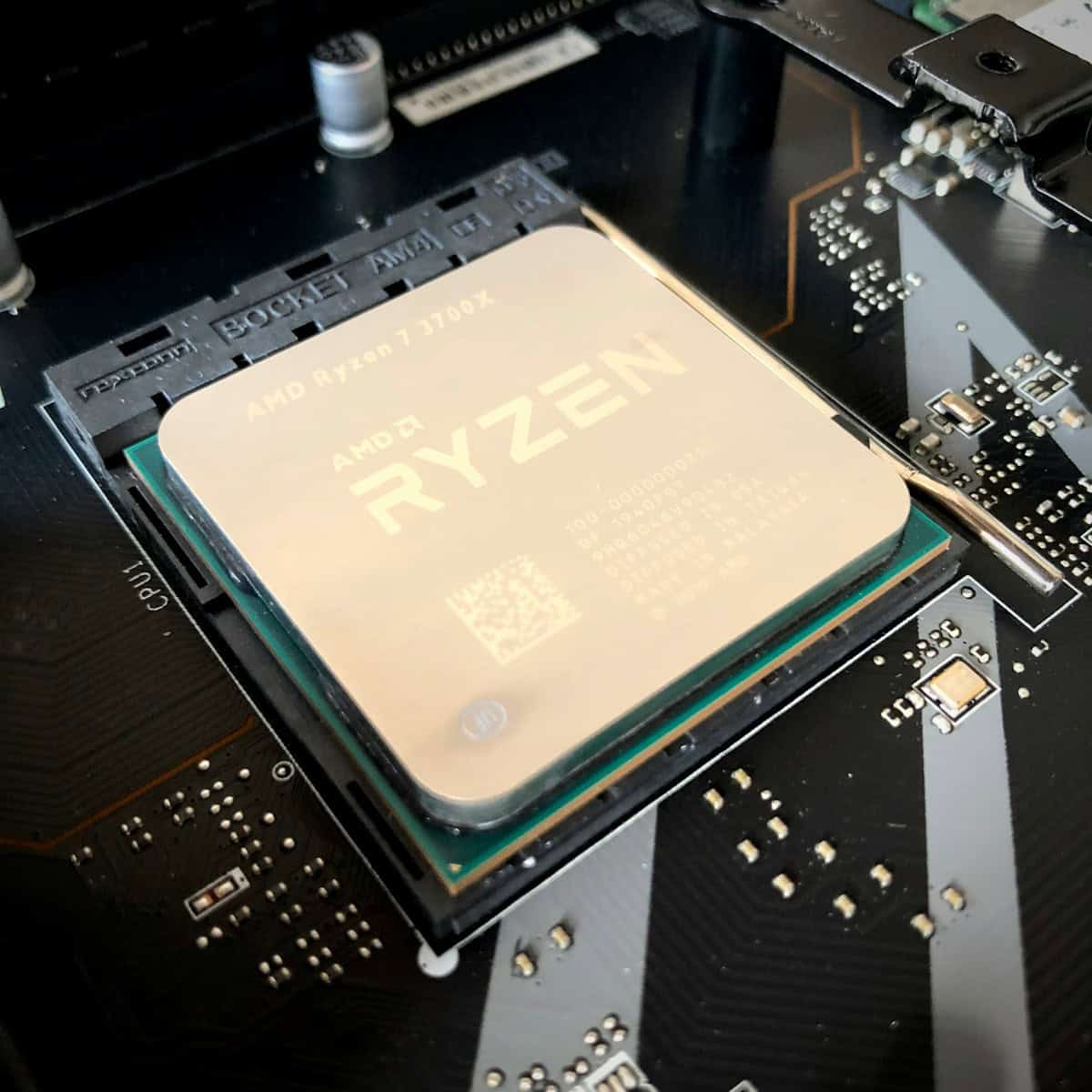
Is your computer running slowly? You can boost your CPU performance with a few simple tricks. Optimizing your processor’s speed can make your PC more responsive and efficient for work, gaming, and everyday tasks.
Many factors affect CPU performance, from software settings to hardware upgrades. Simple steps like adjusting power settings and removing bloatware can have a big impact. More advanced users may want to try overclocking their CPU for extra speed.
Let’s look at some quick ways to rev up your processor:
| Method | Difficulty | Potential Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Update Windows | Easy | Low-Medium |
| Clean CPU fan | Easy | Medium |
| Adjust power plan | Easy | Medium |
| Overclock CPU | Advanced | High |
Fundamentals of CPU Performance
CPU performance depends on various factors that determine how quickly a processor can execute tasks. Understanding these elements helps in optimizing your computer’s speed and efficiency.
Understanding Processor Specifications
Clock speed measures how many cycles a CPU can execute per second. It’s typically expressed in gigahertz (GHz). Higher clock speeds generally mean faster processing.
Core count also plays a crucial role. More cores allow for better multitasking and improved performance in multi-threaded applications.
CPU cache size affects how quickly the processor can access frequently used data. Larger caches usually result in better performance.
Here’s a simple comparison of key CPU specifications:
| Specification | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|
| Clock Speed | Higher is faster |
| Core Count | More cores for multitasking |
| Cache Size | Larger for quicker data access |
Processor power management features like turbo boost can temporarily increase clock speeds for demanding tasks.
Benchmarking CPU Capabilities
Benchmarking helps you measure your CPU’s performance objectively. It allows you to compare your processor against others and track improvements after optimizations.
Popular benchmarking tools include Cinebench, Geekbench, and PassMark. These programs run standardized tests to evaluate your CPU’s single-core and multi-core performance.
When benchmarking, run tests multiple times for consistent results. Compare your scores with those of similar CPUs to gauge relative performance.
Overclocking can boost benchmark scores by increasing the CPU multiplier and core voltage. However, it may reduce system stability and increase power consumption.
Remember that real-world performance often differs from benchmark results. Consider how you use your computer when interpreting benchmark data.
Optimizing Operating System Settings
Adjusting key Windows settings can significantly boost CPU performance. These tweaks focus on power management, background processes, and system updates.
Adjusting Windows Power Options
To maximize CPU performance, modify your power plan settings. Open Control Panel and navigate to Power Options. Select “High Performance” for optimal CPU usage. This plan prioritizes performance over energy savings.
Custom power plans offer more control. Click “Create a power plan” and choose “High performance” as the starting point. Adjust processor power management settings to ensure maximum CPU utilization.
Set minimum and maximum processor state to 100% for constant high performance. Disable CPU parking to keep all cores active. These settings may increase power consumption but will boost overall system speed.
Managing Background Applications
Unnecessary background apps can slow down your CPU. Use Task Manager to identify and close resource-hungry programs. Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc to open Task Manager and sort processes by CPU usage.
Disable startup programs that launch automatically with Windows. In Task Manager, switch to the Startup tab. Right-click on items you don’t need and select “Disable”.
Consider using Windows 10’s built-in “Storage Sense” feature. It automatically removes temporary files and unused data. Enable it in Settings > System > Storage.
| Action | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Close unused apps | Frees up CPU resources |
| Disable startup items | Faster boot times |
| Use Storage Sense | Removes junk files |
Updating System and Drivers
Keep your system and drivers up-to-date for optimal CPU performance. Windows Update handles most system updates automatically. Check for updates manually by going to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
Driver updates are crucial for CPU efficiency. Use Windows Device Manager to check for driver updates. Right-click on devices and select “Update driver”.
For graphics cards, download the latest drivers directly from the manufacturer’s website. This ensures you have the most recent optimizations for your CPU and GPU interaction.
Consider using Windows’ built-in troubleshooters. They can identify and fix common performance issues. Access them through Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot.
Advancing CPU Performance Through Hardware
Upgrading and optimizing hardware components can significantly boost CPU performance. This involves enhancing cooling systems, upgrading key components, and applying effective thermal solutions.
Enhancing Cooling Efficiency
Proper cooling is crucial for optimal CPU performance. A well-designed cooling system helps prevent thermal throttling and extends the lifespan of your processor.
Start by cleaning your computer’s internals with compressed air to remove dust buildup. This simple step can improve airflow and heat dissipation.
Consider upgrading your CPU cooler. Air coolers and liquid cooling systems offer different benefits:
| Cooler Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Air Cooler | Affordable, reliable | Bulky, can be noisy |
| Liquid Cooler | Efficient, quieter | More expensive, risk of leaks |
For most users, a high-quality air cooler provides sufficient cooling. Enthusiasts may prefer liquid cooling for its superior heat dissipation.
Ensure proper case airflow by arranging fans for optimal intake and exhaust. This creates a consistent flow of cool air across components.
Upgrading to Superior Hardware
Upgrading key components can remove bottlenecks and unlock your CPU’s full potential.
Start with RAM. More memory allows your CPU to handle larger datasets efficiently. Faster RAM speeds can also improve overall system responsiveness.
Consider upgrading your motherboard if it’s limiting your CPU’s capabilities. Newer chipsets often support faster RAM and provide better power delivery.
Graphics cards can offload certain tasks from the CPU. A powerful GPU can improve performance in graphics-intensive applications and games.
For storage, an SSD can dramatically reduce load times and improve system responsiveness. This allows your CPU to access data more quickly.
Applying Quality Thermal Solutions
Effective thermal management is key to maintaining peak CPU performance.
Apply high-quality thermal paste between the CPU and cooler. This improves heat transfer and lowers operating temperatures. Reapply paste every few years as it can dry out over time.
Consider using thermal pads on other heat-generating components like voltage regulators. This helps distribute heat more evenly across the system.
For extreme performance, some enthusiasts use liquid metal as a thermal interface. While highly effective, it requires careful application to avoid damage.
Monitor your CPU temperatures using software tools. This helps you identify potential cooling issues before they impact performance.
Advanced Techniques for Expert Users
Maximizing CPU performance requires advanced methods. These techniques involve BIOS adjustments, manual overclocking, and stability testing. They offer significant gains but demand careful implementation.
Tweaking BIOS Settings for Performance
Access your motherboard’s BIOS to unlock hidden performance potential. Disable power-saving features like C-states and EIST for consistent clock speeds. Enable XMP profiles for RAM to run at advertised speeds. Adjust CPU voltage and multiplier settings for modest performance boosts.
Set a more aggressive fan curve to improve cooling. This helps prevent thermal throttling and maintains higher clock speeds. Review your motherboard manual for specific BIOS options.
Be cautious when changing settings. Small increments are safest. Record your changes in case you need to revert them.
Manual Overclocking for Additional Power
Manual overclocking pushes your CPU beyond stock speeds. Start by increasing the CPU multiplier in small steps. Test stability after each increase. If stable, continue until you reach your desired performance or temperature limit.
Adjust CPU voltage (VCore) if needed. Higher clocks often require more voltage. Be careful – too much voltage can damage your CPU. Use this table as a general guide:
| Overclock Level | Voltage Increase | Temperature Increase |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | 0.05V – 0.10V | 5-10°C |
| Moderate | 0.10V – 0.15V | 10-15°C |
| Aggressive | 0.15V – 0.20V | 15-20°C |
Monitor package temperature closely. Keep it under 80°C for long-term stability.
Monitoring and Stress Testing for Stability
After overclocking, thorough testing is crucial. Use stress test software like Prime95 or AIDA64 to push your CPU. Run tests for several hours to ensure stability.
Monitor temperatures, clock speeds, and voltages during testing. Tools like Intel’s Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) provide detailed information. Watch for crashes, freezes, or unexpected throttling.
If instability occurs, reduce clock speed or increase voltage slightly. Retest until you find a stable configuration. Remember, every CPU has different overclocking headroom.
Regular use of monitoring tools helps catch potential issues early. Adjust your overclock as needed to maintain long-term stability and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
CPU performance optimization involves various strategies across different platforms and scenarios. These methods range from software tweaks to hardware adjustments, each tailored to specific needs and systems.
What steps can be taken to enhance CPU performance when gaming?
To boost CPU performance for gaming, start by closing unnecessary background programs. Update your graphics drivers regularly.
Adjust in-game settings to reduce CPU load. Consider overclocking your CPU if your system allows it.
How can one optimize CPU performance on a Windows 10 system?
Improve Windows 10 CPU performance by disabling startup programs you don’t need. Use the Task Manager to identify and close resource-heavy applications.
Update Windows and drivers regularly. Adjust your power plan to favor performance over energy saving.
Which methods improve CPU utilization in Windows 11?
For Windows 11, maximize CPU performance by tweaking power settings. Open Control Panel, select Power Options, and choose “High performance” mode.
Clear temporary files and defragment your hard drive. Use the built-in Windows troubleshooter to identify and fix performance issues.
What strategies boost CPU performance on Android devices?
On Android, limit background processes through the Developer Options menu. Uninstall unused apps to free up system resources.
Keep your device updated. Use a reputable cleaner app to remove junk files and clear cache regularly.
Through BIOS settings, how can processor speed be accelerated?
Access your BIOS settings during startup. Look for CPU or Processor settings and find the option to adjust clock speed.
Increase the CPU multiplier gradually. Monitor temperatures closely to avoid overheating. Adjust voltage settings if necessary, but do this cautiously.
What actions can resolve issues of suboptimal CPU performance?
Address poor CPU performance by checking for malware. Run a full system scan with updated antivirus software.
Clean your PC’s internals to improve airflow. Apply new thermal paste to your CPU if temperatures are high.
| Action | Benefit | Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| Update drivers | Improves compatibility | Easy |
| Close background apps | Frees up resources | Easy |
| Overclock CPU | Boosts speed | Advanced |
| Clean PC internals | Better cooling | Moderate |
| Adjust power settings | Optimizes performance | Easy |